CPOM2015 23rd November 2017
A new paper in Advances in Space Research, led by Rachel Tilling, provides a first look at 2017 Arctic sea ice volume from CryoSat.
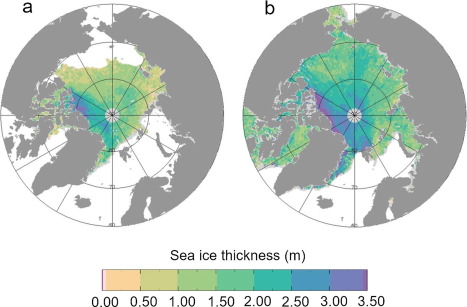
Northern Hemisphere sea ice thicknesses as measured by CryoSat-2. The maps show sea ice thickness for (a) autumn (October/November) 2016 and (b) spring (March/April) 2017. These correspond to the start and end of the 2016–2017 sea ice growth season, respectively. Thicknesses are shown at 60°N and above, where the majority of ice is located.
Using data from CPOM’s sea ice processor, which has been under constant development at CPOM since the early 1990s, the 7 year time series also shows large year-on-year variations in the volume of sea ice which persists in the Arctic year round: between 2010 and 2012, volume declined by 31%, followed by an 89% increase in 2013 and then a 27% decrease from 2013–2016.
These changes impacted on the total autumn sea ice volume, which declined by 14% between 2010 and 2012, increased by 42% in 2013, then decreased by 25% from 2013–2016. The peak autumn volume in 2013 was seen as thick ice cover in the region north of Greenland and Ellesmere Island, with ice being 17% thicker than average, associated with a 5% drop in the number of days on which melting occurred – conditions more typical of the late 1990s. The sharp increase in sea ice volume after just one cool summer demonstrates the ability of Arctic sea ice to respond rapidly to a changing environment.
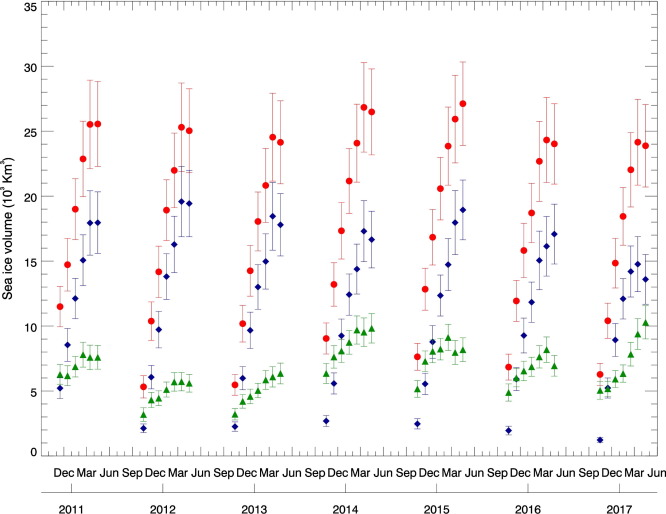
Cryosat-2 estimates of total (red stars), first-year (blue diamonds) and multi-year (green triangles) sea ice volume. Also shown are model estimates of volume from the Pan-Arctic Ice-Ocean Modelling and Assimilation System (PIOMAS) (black line)
The paper also provides a comprehensive description of the data processing steps that CPOM uses to estimate Arctic sea ice thickness and volume from CryoSat’s radar altimetry data, along with associated uncertainties.
Next steps include testing the method on sea ice thickness retrievals in the Antarctic and developing sea ice processing systems for other satellites monitoring the polar regions.
The full paper Estimating Arctic sea ice thickness and volume using CryoSat-2 radar altimeter data is available now in Advances in Space Research.
